
Floods are among the most common and destructive natural disasters, impacting homes and communities worldwide. Rainbow Restoration highlights key flood facts:
|
Key Takeaways:
- Floods are the most common type of natural disaster in the United States.
- New land developments increase flood risks because there’s nowhere for water to go.
- Flood-related insurance claims increased by 660% from 2000-2020.
As the most common natural disaster globally, floods can happen anytime, anywhere. They cause substantial damage each year and can have lasting impacts on society, properties, and the environment.
Learn about critical flooding facts –– from common causes to the biggest risk factors –– what flood zones are, and how to prepare for flooding.
Table of Contents:
- Types of Floods: Basic Facts About Floods
- Frequency: How Often Do They Occur?
- Causes: How Does a Flood Form?
- Risks: What Are Flood Zones?
- Restoration Facts: What Damage Does a Flood Cause?
- Flood Preparedness Checklist
- Tips for Recovering from Flood Damage
- Call Rainbow Restoration® for Water Damage Mitigation
- Flooding FAQ
Methodology: Rainbow Restoration compiled these facts about flooding from a range of news, government, and research articles. The primary source of information on flooding is the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), which provides resources and data about disasters.
Types of Floods: Basic Facts About Floods
Every American is at risk of experiencing a flood — whether from a weather event or a burst pipe in a building. Floods can both be a nuisance and dangerous. Here are some common facts about flooding, different types of floods, and their potential dangers:
- Floods are the most common type of natural disaster in the United States. (NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory)
- There are many different types of floods, including river floods, coastal floods, storm surges, inland flooding, flash floods, and debris flows. (NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory)
- Environmental flooding can be broken into three main categories: flash flooding, river flooding, and coastal flooding. (FEMA)
- A person can be knocked down by just 6 inches of fast-moving water, and 12 inches can carry away most vehicles. (National Weather Service)
.webp)
Frequency: How Often Do They Occur?
Floods are becoming increasingly common as climate change impacts weather patterns. Both increased rain and instances of drought impact the risk of floods.
- In 2023, the United States experienced extreme rates of precipitation in the form of atmospheric rivers, as well as droughts across different areas of the country. (NOAA)
- The risk of floods is increasing due to factors associated with climate change, such as higher sea levels, greater risks of forest fires, changes to precipitation patterns, and more. (FEMA)
- Drought increases the risk of flooding, as too-dry soil struggles to absorb water. (Environmental Defense Fund)
Causes: How Does a Flood Form?
Some areas of the country are more prone to flooding than others. Urban zones, for example, may flood more frequently because of the lack of natural runoff routes. Areas close to the ocean or a river are also more prone to flooding. FEMA calls these high-risk areas 100-year floodplains, as there is a 1% chance that the area will flood at any given time within the year.
Here are facts about the primary causes of floods:
- New land development or urbanization is a source of flooding, as it disrupts natural runoff routes. (USGS)
- Floods have numerous causes, including heavy rain, spring thawing, snow melt runoff, flash flooding, and mudflows. (FEMA)
- The causes of floods are interconnected in that adverse weather, such as heavy rains, can cause flooding, which contributes to infrastructure issues such as dams and levees failing, causing further flooding. (FEMA)
- Floods on a residential or commercial property can also be caused by burst pipes, leaky faucets, or worn toilet flappers. Approximately 10% of homes lose 90 gallons or more of water a day from leaks. (EPA)
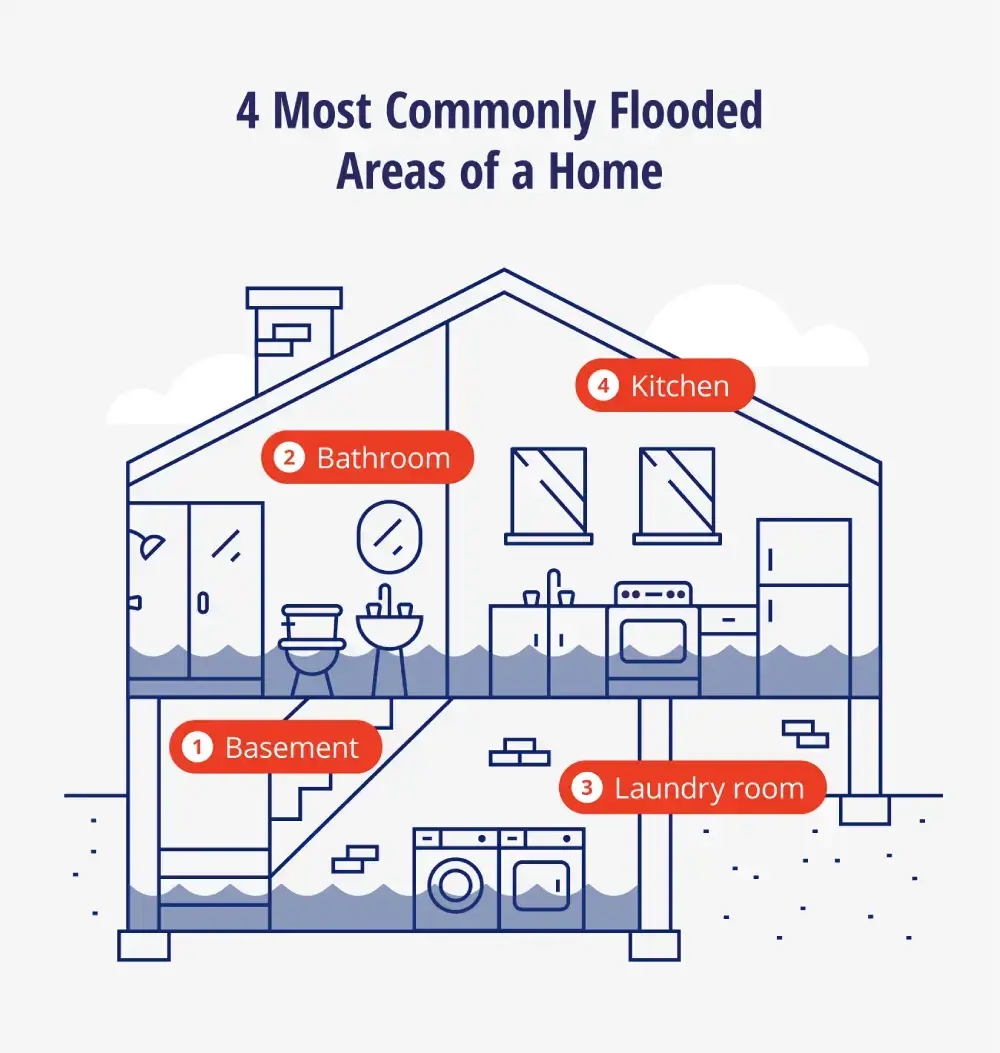
Risks: What Are Flood Zones?
Flood zones are areas most prone to flooding. This includes coastal areas, places downstream from dams or levees, close to rivers, and urban areas. Here are some flood statistics about flood zones:
- Nine percent of properties in the United States are within 100-year flood zones. (Congressional Budget Office)
- Properties in 100-year flood zones are more than twice as likely to experience damage from a flood than a fire. (Arkansas Department of Agriculture)
- Basement floods are the most common residential flooding location, followed by washrooms, laundry rooms, and kitchens.
- Texas experiences the most damage from flooding, followed by New Jersey and Louisiana. (FEMA)

Restoration Facts: What Damage Does a Flood Cause?
Floods wreak havoc on residential and commercial properties. Homes and buildings can be submerged, causing ample damage and impacting the structural integrity. . Rising waters can ruin furniture, appliances, and belongings. Electrical systems can also be compromised, posing a serious safety hazard.
Floodwaters often carry raw sewage and contaminants, requiring extensive cleaning and disinfection by professionals. Here are some statistics about flood damage:
- Only 1 inch of water can cause more than $25,000 worth of damage to a home. (FEMA)
- Floods cost somewhere between $179.80 and $496 billion dollars in damage each year in the United States. (Joint Economic Committee)
- NFIP insurance claims increased by 660% from 2000-2020. (FEMA)
Flood Preparedness Checklist
While floods can strike at any time and for any number of reasons, it’s important to be prepared, particularly if living in a high-risk zone. As a property owner or facility manager, it’s critical to be ready with the following flood safety tips:
- Create an emergency kit that includes essential items, including but not limited to:
- First-aid kit
- Essential medications
- Enough food and water for at least three days
- Copies of government-issued identification
- Batteries
- Portable charger
- Have an emergency plan that includes where to seek shelter and emergency contacts.
- Ensure the property is well maintained and regularly inspected for any signs of water damage.

Tips for Recovering From Flood Damage
In the aftermath of a flood, the damage and disruption can feel overwhelming. Focus first on prioritizing safety and well-being. Remember, professional help is invaluable in navigating flood recovery and remediation.
Recovery tips when facing flood damage:
- Prioritize safety. Get medical attention if required and avoid any unnecessary travel and exposure to elements.
- Wait for official clearance. Determine if the space is safe to be in; if not, find temporary shelter.
- Contact your insurance carrier to report any losses as soon as possible to start the claims process.
- Consult with restoration professionals. For major restoration work from storm damage or other flooding, like electrical repairs, structural assessments, or mold remediation, consult with the qualified service professionals at Rainbow Restoration.
Call Professionals for Water Damage Restoration
If you experience a flood from a natural disaster or plumbing-related issues, always prioritize safety and let professionals handle any water damage and flood repairs.
Trust Rainbow Restoration in times of crisis — Restoration begins now.® Call today for water damage restoration services.
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and may not be applicable to every situation. You are responsible for determining the proper course of action for your property. Services should be performed by licensed and experienced professionals. Rainbow Restoration is not responsible for any damages that occur as a result of this blog content or your actions. For the most accurate guidance, contact a Rainbow Restoration professional for a custom, on-site assessment.
Flooding FAQ
What Is a Flash Flood?
The National Weather Service defines flash flooding as a flood caused by heavy rainfall that happens quickly, with flooding occurring within minutes or a few hours of excessive rainfall.
How Long Can Floods Last?
Depending on the type of flood, it can start and be over within minutes, such as a flash flood. Depending on the severity, floods can also last days, weeks, or even months.
Where Are Floods Most Common?
Urban areas are more likely to flood, as they have more concrete and are less likely to absorb moisture. According to the Weather Channel, urban areas of Texas have the highest instances of flooding. Areas on the East Coast of the United States are most likely to experience flooding associated with hurricanes.
What Is the Biggest Flood in History?
The biggest flood in American history was in Mississippi in 1993, in what is known as the Great Flood of 1993, with the river cresting in the St. Louis area at 49.6 feet.
What Are the Effects of Floods?
Floods can cause property damage, power outages, interrupt transportation, and pollute drinking water.

